Variational Sparse Coding
Implementation of the “Variational Sparse Coding” paper as part of the ICLR 2019 Reproducibility Challenge. [pdf] [oral presentation] [slides] [poster] [code] [peer reviews] [reviewers]

Implementation of the “Variational Sparse Coding” paper as part of the ICLR 2019 Reproducibility Challenge. [pdf] [oral presentation] [slides] [poster] [code] [peer reviews] [reviewers]

Sequence-to-sequence recurrent neural network (bidirectional LSTM) with Global Attention (Luong et al., 2015) and Beam Search implemented in PyTorch. ~41 BLEU in 110K-sentences English-Spanish corpus. [code]
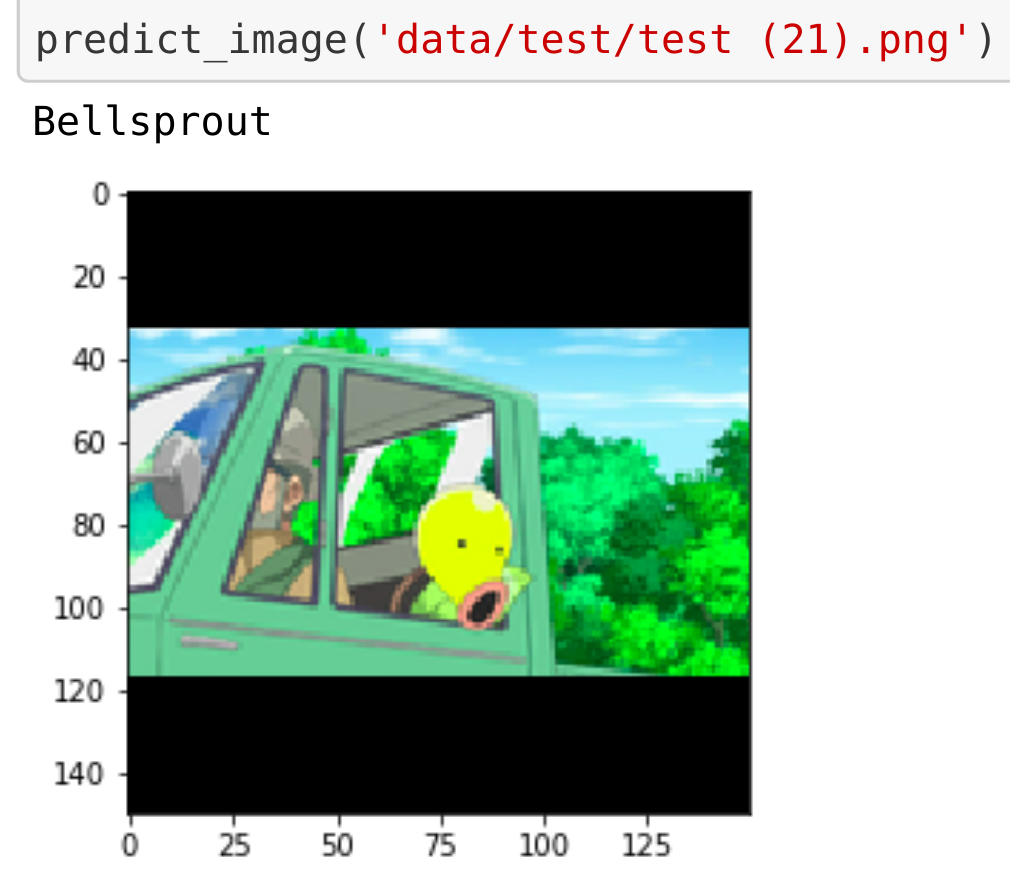
Pokémon image classification with transfer learning from ImageNet-pretrained MobileNet convolutional neural network (Howard et al., 2017). ~82% accuracy with 27 classes and 3.8K web-scraped images. Deployed in Flask with React JS for the SPA user interface. Presented at Infosoft 2017 and Hack Faire 2017. [slides] [demo] [code]
Published in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), 2018
Feature selection is an important step in gene expression data analysis. However, many feature selection methods exist and a costly experimentation is usually needed to determine the most suitable one for a given problem. This paper presents the application of gradient boosting and neural network techniques for the construction of metamodels that can recommend rankings of {feature selection - classification} algorithm pairs for new gene expression classification problems. Results in a corpus of 60 public data sets show the superiority of these techniques in producing more useful rankings in relation to classical metamodels.
Download here
Published in ReScience C, 2019
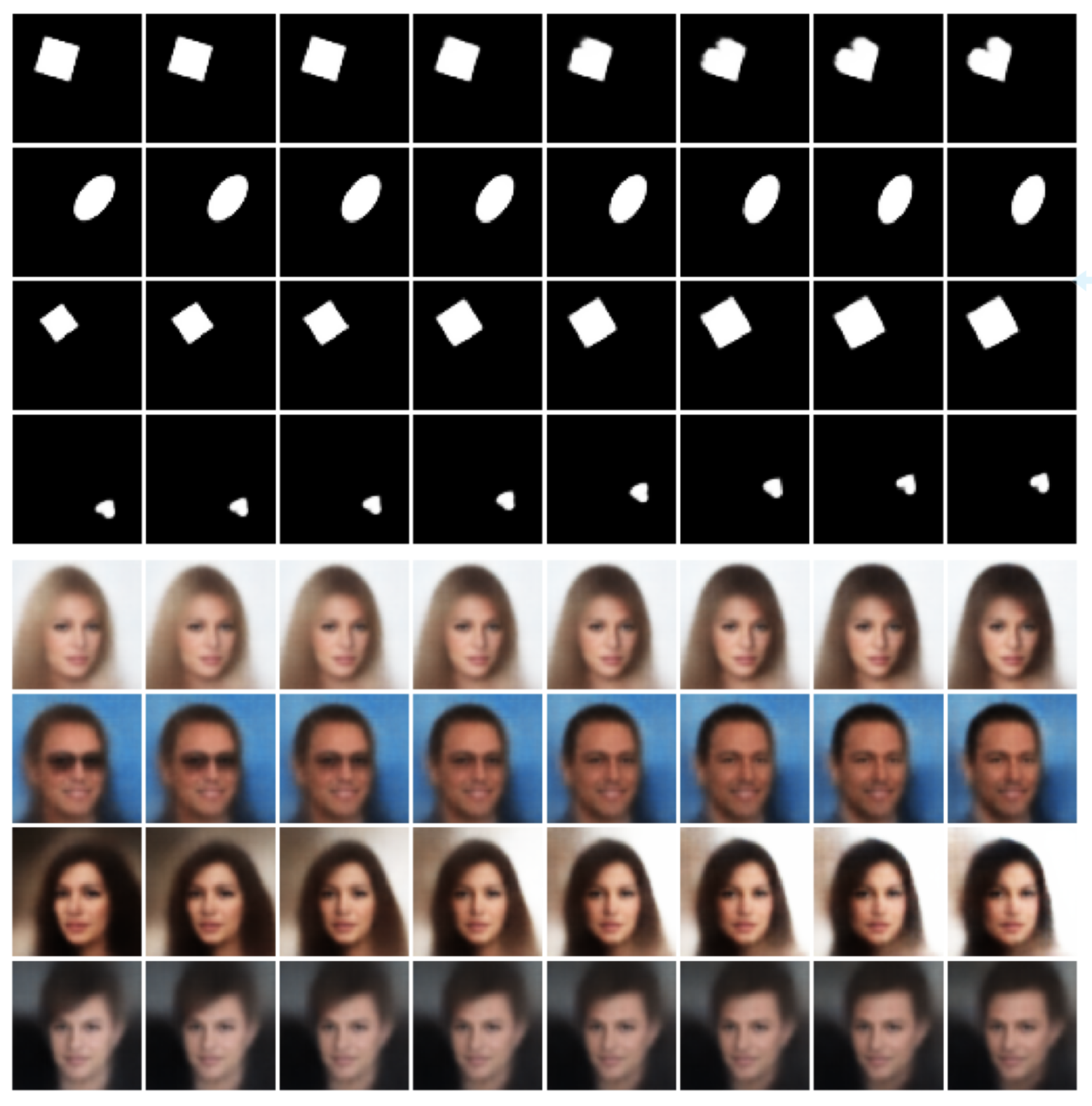
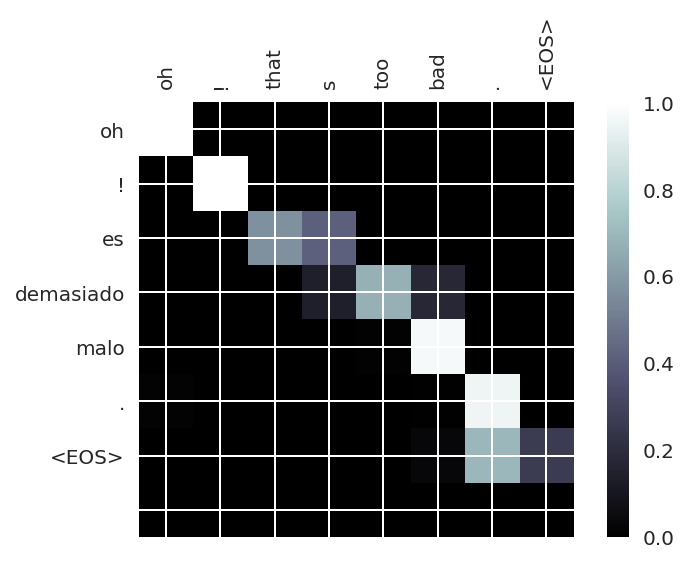
The reproduced paper proposes an improvement over the Variational Autoencoder (VAE) architecture by explicitly modelling sparsity in the latent space with a Spike and Slab prior distribution and drawing ideas from sparse coding theory. The main motivation behind the original work lies in the ability to infer truly sparse representations from generally intractable non-linear probabilistic models, simultaneously addressing the problem of lack of interpretability of latent features. Moreover, the proposed model improves the classification accuracy using the low-dimensional representations obtained, and significantly adds robustness while varying the dimensionality of latent space.
Download here
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.